Introduction
In this Web service article series, we
will learn about - What Asp.net Web services are? And How to create and consume
web services in a client application?
What is Asp.net Web Services?
Asp.net Web services is a
communication strategy by which two applications present at the same or different
location can communicate easily as long as they are connected by a network.
Web services are created with an
extension of .asmx. Hence, Asp.net Web services are also known as ASMX
services. Here, .asmx stands for Active server method extension. Web services
came into play when we need to access some method which can be present on the same
computer or the different computer.
Web services worked on open standard
& protocols. They used SOAP web protocol. SOAP enables an operating system
to communicate data written in XML over HTTP. XML (i.e. Extensible Markup
Language) which is platform independent language to send data over internet and
HTTP protocol is for sending and receiving messages over the internet. For
example- Suppose I create a web service in Java which can be used by the
application built using .Net. And also services built on .Net can be consumed
by Java application.
Some related terms
and concept in web services: -
o ASMX: Active Server Method
Extension. ASMX services give a way for developing interoperable application
i.e., enabling an application to invoke a method of another application.
o TCP/IP: TCP/IP is a combination of
two separate protocols- Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. This
is the basic communication protocol or language of the internet. Three most
commonly TC/IP protocol:
o HTTP: Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
is used to send and receive messages, over non-secure data transmission. A web
client (browser) sends a request message to the web server. The web server
receives the request and sends the response back to the web client.
o HTTPS: HTTP functionality is
enhanced by providing secure data transmission. Information like account
details and bank transaction need to done using this from client to server.
o FTP: File Transfer Protocol is
used to send files directly from one computer to other.
o SOAP: SOAP stands for Simple
Object Access Protocol. SOAP protocol is used to provide enveloping the message
which needs to be transmitted over the network. SOAP envelope contains two
parts:
 |
| SOAP Architecture |
o SOAP Header: Provide
information about the message authentication, encoding the data and how the receiver
should process the message.
o SOAP Body: SOAP body
contains data in WSDL document. It contains methods that are exposed by the web
service, the parameter, and their types and return types of the methods.
The
message format of SOAP usually relies on HTTP and uses other protocols of
different application layers. Among these the most notable application layer is
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) and HTTP. SOAP forms the foundation layer for web
services.
o WSDL: Web Service Description
Language which is pronounced as Wis-del. This is used to describe a web service
based on XML. WSDL contains all information about the service, its residing
location and the way of consuming the service.
o UDDI: UDDI Stands for Universal
Description Discovery and Integration. This is used to publish and discover the
information about the web services. It is an XML based standard.
o Serialization: Serialization
is the process of converting an object into a stream of bytes so that it can be
transported across the network and in order to store the object into the CACHE memory,
a database or file. Its main aim is to save the state of an object in order to
be able to recreate it when needed.
o De-serialization: The
reverse process of serialization is called deserialization. The information in
bytes is again recollected into the object. When the object is deserialized, an
exact copy of the original object is created.
o Uses of Serialization: Usages of
serialization perform various actions: -
o Sending
the object to a remote application by means of a web service,
o Passing
an object from one domain to another,
o Passing
an object through the firewall as an XML string
o Maintaining
security or user specific information across an application.
o Namespace: The System.Web.Services.WebServices; namespace is used to build web service.
o Is XML case sensitive or not?
Yes,
XML tags are case sensitive. The tag <Header> is different from the tag
<letter>. Opening and closing tags must be written with the same case.
For
example-
///This
is incorrect way to writing XML tags.
<Letter>Hello,
Imagination hunt Readers<letter>
///This
is correct way to writing XML tags.
<Letter>Hello,
Imagination hunt Readers<Letter>
“Opening
and closing tags” are often referred to as “Start and End tags”.
For any
query, comment us below.
Next – Asp.net Web Services
#2
Keep learning and sharing...

 Technologies
Technologies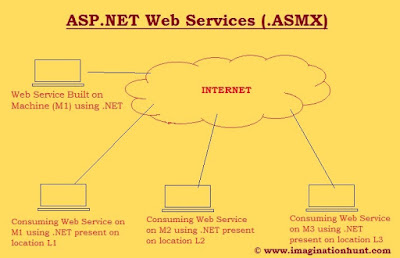

No comments:
Post a Comment